Diamond Education
Our comprehensive diamond education guide is designed to answer all your diamond-related queries. We go beyond the 4 C's of diamonds (carat, cut, colour, and clarity) to help you make an informed diamond purchase while maximising the appearance and value of your diamond.
What is a diamond?
Diamond is one of the world's most precious gemstones, known for its extraordinary hardness, brilliance, and durability. It is the crystallized form of carbon. Carbon crystallizes hundreds of miles below the Earth's surface in the most robust and symmetrical cubic structure.
The 4 C’s
The 4Cs - cut, colour, clarity, and carat weight - are a universal language established in partnership with the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) to simplify diamond grading. These four diamond characteristics are the most significant in determining its beauty and structure. The combination of these elements determines the relative rarity and value of a diamond.

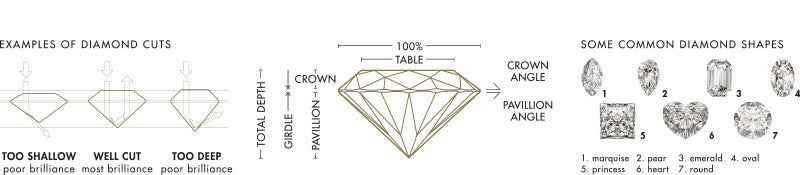
Cut
A diamond's dimensions and symmetry are what genuinely distinguish its cut. The proportions of your diamond significantly impact how brilliantly it sparkles. To create an "ideal cut" diamond that allows the most excellent light to pass through the top of the stone, the depth, table size, crown height and angle, girdle thickness, and other parameters are considered. The terms "cut" and "shape" of a diamond are usually used interchangeably, such as round brilliant or princess cut.
Colour
Diamonds can be colourless or have a slight yellow tint. Diamond hues are categorised from D through Z. BSD Jewels, on the other hand, offer diamonds rated from D to M and are classified into five broad categories: colourless, nearly colourless, faint, very light, and light. Diamonds with the least amount of colour are preferred while shopping for diamonds. Diamonds with no colour and clarity between D and F on the colour scale are the clearest. Diamonds ranging from D to F are the rarest and most expensive on the scale.

Clarity
A diamond's clarity is determined by its inherent inclusions, typically microscopic size." The clarity of a diamond is determined by the imperfections linked with it, according to expert analysts. Diamond clarity refers to the degree to which these imperfections are present on or inside the diamond and ranges from FL (Flawless) to I (Incomplete) (Included). Diamonds that are free of such flaws are of exceptional quality. Diamonds from Divine Solitaires range in quality from IF (Internally Flawless) to SI2 (Slightly Included 2).

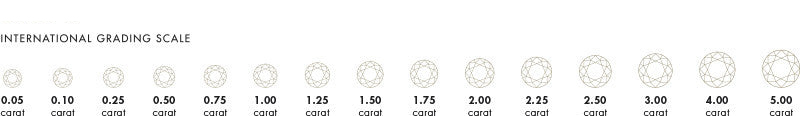
Carat
A diamond's weight is measured in carats. The term "carat" was derived from the term "carob seeds," which was used to quantify the value of diamonds before the twentieth century. A half carat (0.50 carat) is, therefore, equal to 0.10 grammes. 1 gramme, on the other hand, equals 5.00 carat. The greater the carat weight, the more unique the diamond and, thus, the higher the price. A diamond's weight is measured in carats. The weight is rounded to the nearest two decimal places as one carat equals 0.2 grammes, the higher the price.